Table of Contents
In an era increasingly defined by the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, fuel cells stand at the forefront of a technological revolution poised to reshape our relationship with power. As the world grapples with climate change and dwindling fossil fuel reserves, these quiet yet powerful devices offer a glimpse into a cleaner, more efficient future. By harnessing the chemical energy of hydrogen and other fuels, fuel cells convert it directly into electricity, presenting a viable alternative that complements the renewable energy landscape. This article delves into the mechanics of fuel cells, their applications across various sectors, and their pivotal role in accelerating the transition to a greener economy. Join us as we explore how fuel cells are not just a component of the renewable energy revolution—they are essential to its very foundation.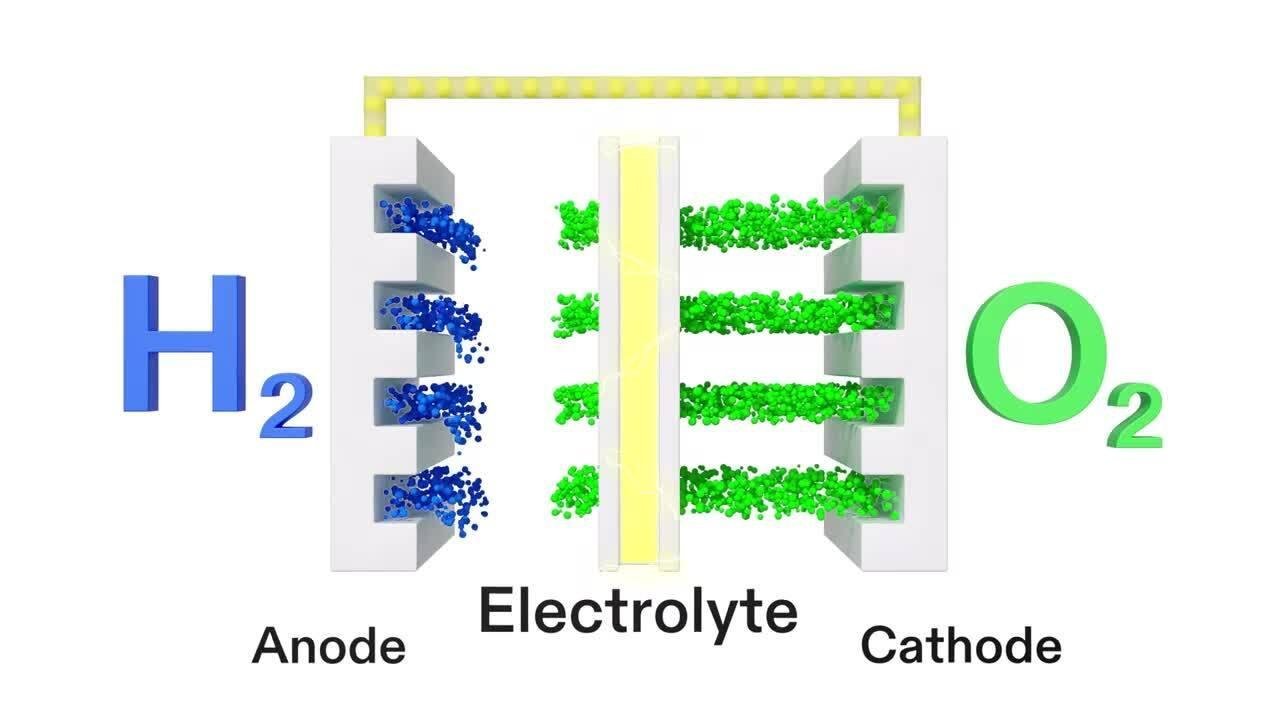
Exploring the Science Behind Fuel Cells and Their Role in Energy Transition
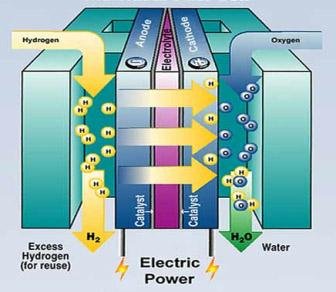
Fuel cells are at the forefront of clean energy technology, offering a viable solution for the transition from fossil fuels to sustainable energy sources. These devices convert chemical energy into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction, primarily using hydrogen and oxygen as fuel sources. The process is both efficient and clean, producing only water and heat as byproducts. The versatility and scalability of fuel cells make them suitable for various applications, from powering vehicles to providing backup energy for hospitals, further supporting their role in developing a resilient energy system.
As the world moves towards decarbonization, fuel cells present significant advantages in integrating renewable energy. By storing excess energy generated from sources like wind and solar, fuel cells can help mitigate the intermittency of these resources. This leads to more stable and reliable energy supply chains. Consider the following key benefits of fuel cells in renewable energy systems:
- Grid Stability: Providing backup power during fluctuations.
- Energy Storage: Converting surplus energy into hydrogen for later use.
- Low Emissions: Contributing to cleaner air standards.
- Diverse Fuel Options: Compatibility with various hydrogen sources.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Efficiency | Minimizing energy loss in the conversion process. |
| Modular Design | Allowing for tailored energy solutions based on needs. |
| Reduced Dependency | Less reliance on traditional fossil fuel infrastructures. |
Innovative Applications of Fuel Cells in Transportation and Industry
Fuel cells are increasingly recognized for their versatility, enabling a transition away from traditional fossil fuels across various sectors. In the transportation industry, they are being utilized to power everything from public buses to private vehicles, providing a clean alternative to conventional engines. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) are known for their quick refueling time and impressive range, making them a viable option for long-distance travel. Highlights of fuel cell applications in transportation include:
- Public Transit: Many cities are incorporating hydrogen fuel cell buses into their fleets, reducing emissions and improving air quality.
- Trucking: Heavy-duty trucks are now operating on fuel cells, offering a sustainable solution for logistics and freight movement.
- Shipping: Fuel cells are being tested in maritime applications, promising cleaner ocean transportation.
In the industrial sector, fuel cells are revolutionizing the way energy is produced and consumed. They’re not only providing power for manufacturing processes but also serving as backup systems and auxiliary power units (APUs). Notably, industries such as construction, mining, and aerospace are leveraging fuel cell technology to enhance efficiency and sustainability. Consider the following applications:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Construction | Power tools and equipment with hydrogen fuel cells to reduce emissions on job sites. |
| Mining | Use of fuel cells in underground mining vehicles, offering cleaner operations and improved safety. |
| Aerospace | Hydrogen fuel cells as auxiliary power units for reducing aviation’s carbon footprint. |

Overcoming Challenges: Infrastructure and Economic Viability for Widespread Adoption
The transition to a sustainable energy future hinges on several infrastructure challenges that must be addressed to ensure the widespread adoption of fuel cell technology. Investment in hydrogen production and distribution networks is crucial, as the current infrastructure is largely focused on fossil fuels. To facilitate this shift, we need to develop integrated systems that can produce hydrogen from renewable sources, making it both efficient and cost-effective. Technological advancements are required not only in fuel cell design but also in the storage and transportation of hydrogen, ensuring that it can compete with established energy sources on both cost and functionality.
Moreover, the economic viability of fuel cells plays a pivotal role in their adoption across industries. To stimulate growth in this sector, it is essential to establish favorable policies and incentives that encourage investment in fuel cell technology. A collaborative approach involving governments, private sectors, and research institutions could unlock funding opportunities and drive innovation. An analysis of costs and benefits reveals that while initial investments may be high, the long-term savings and environmental benefits can significantly outweigh these costs. A streamlined approach could include:
- Tax credits for fuel cell manufacturers
- Subsidies for research and development
- Public-private partnerships to create pilot projects
For example, cost breakdowns of traditional vs. fuel cell technologies illuminate the potential for scalability as market demand grows:
| Technology | Initial Cost (per kW) | Operational Cost (per year) | Lifespan (years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Fossil Fuels | $1,200 | $100,000 | 25+ |
| Fuel Cells | $800 | $50,000 | 20+ |

Future Trends: Integrating Fuel Cells into Sustainable Energy Solutions
As the global push towards decarbonization intensifies, fuel cells are poised to play a pivotal role in integrating with various sustainable energy solutions. Their unique ability to generate electricity through chemical reactions, rather than combustion, offers a clean alternative to traditional power sources. This technology holds significant promise for a variety of applications, from powering electric vehicles to providing backup energy for residential and commercial buildings. Fuel cells can also be paired with renewable sources, such as solar and wind, to create hybrid systems that enhance energy reliability and efficiency. By utilizing fuel cells, we can optimize the intermittent nature of renewables and ensure a steady, dependable energy supply.
The future landscape of energy generation is likely to see fuel cells and renewables working in harmony, creating a multifaceted energy ecosystem. Several key trends are emerging in this synergy:
- Hydrogen Production and Storage: Advancements in electrolysis technology can enable efficient hydrogen production from excess renewable energy.
- Microgrid Development: Fuel cells can enhance the resilience of microgrids, allowing them to operate independently when required.
- Smart Grid Integration: Integrating fuel cells with smart grid technology can lead to optimized energy distribution and management.
| Application | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Transportation | Zero-emission vehicle operation |
| Backup Power | Reliable energy during outages |
| Renewable Integration | Improved energy storage and usage |
In Conclusion
As we stand on the brink of an energy renaissance, fuel cells emerge as a luminous beacon of possibility, illuminating pathways to a cleaner, more sustainable future. Their ability to convert hydrogen and other fuels into electricity with remarkable efficiency holds the promise of transforming our energy landscape, one molecule at a time. As innovations continue to unfold and investments in this technology grow, we find ourselves witnessing a pivotal moment in the renewable energy revolution.
In the journey toward decarbonization, fuel cells are not merely a complement to other renewable sources; they represent a critical cornerstone in our quest for energy independence and environmental stewardship. As we embrace this technology, the challenge lies in fostering collaboration, advancing research, and deploying infrastructure that will support widespread adoption.
The road ahead may be fraught with challenges, yet it is paved with opportunity. As we harness the potential of fuel cells, we are not just powering our cities and industries; we are also fueling a vision—a collective aspiration for a world where energy is abundant, clean, and sustainable. Together, let us embark on this transformative journey, where innovation meets necessity, and where every step toward a greener future is illuminated by the quiet strength of fuel cells.



